Jalpura Khasra no. 439,440, Sector-1 Greater Noida,
Gautam Buddha Nagar, Uttar Pradesh,201306
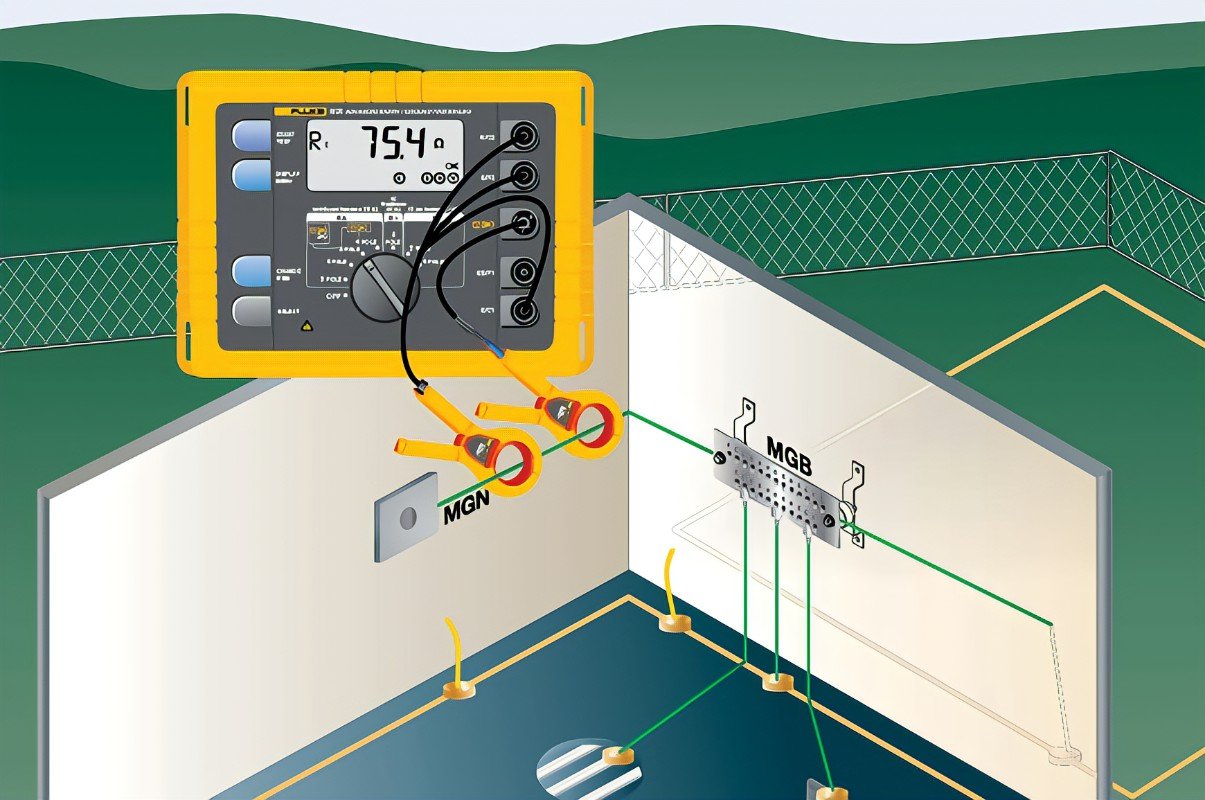
Testing Earthing Resistence
Steps to Measure Earth Resistance:
- Preparation: Disconnect the earthing system from the power supply to avoid interference during the testing process.
- Positioning Electrodes: The Earth Tester uses three or four terminals for measurement. A known distance is maintained between the main earth electrode (the one being tested) and two auxiliary electrodes (P for potential and C for current) driven into the ground.
- Measurement: The Earth Tester injects a current through the current electrode (C), and the potential electrode (P) measures the voltage drop between the main earth electrode and the auxiliary electrodes. The tester calculates the resistance using Ohm's Law (R = V/I).
- Result Interpretation: The earth resistance value is displayed on the tester. Ideally, a low resistance value (typically less than 1 ohm for critical installations) indicates an effective earthing system
Regular testing of earth resistance is crucial for maintaining the safety and performance of earthing systems, particularly in industrial settings.